Animal tissues
Activity-1:
Collect the substance lining the mouth
by using wooden spoon and observe this
under the microscope. Draw the diagram
that you have observed in the microscope,
in your note book.
How are the cells arranged?
Are there any inter cellular spaces?
The epithelial tissue, extremely thin
and flat, form a delicate lining. This is called
as squamous epithelium. We find this type
of epithelium in oesophagus, lining of
mouth, lining of blood vessels, lung alveoli
where transportation of substances
selectively occurs through permeable
membrane (you will learn about
permeability in the next chapter of
“Transport across Membrane)”.
The epithelial cells in skin are arranged
in the form of layers. This is called as
stratified squamous epithelium.
Think, why are the epithelial cells
in the skin are arranged in the form
of layers?
If you drink hot tea or chilled cool
drink, how do you feel?
If your skin burns or is wounded
which tissue would get effected?
Activity-2:
Take a permanent slide of cuboidal
epithelium from your laboratory slide box
and observe under the microscope. Draw
the picture in your note book. How are the
cells arranged?
These are the cuboidal epithelial cells
which form the lining of organs or tubules
like ureters or other parts and provide
mainly mechanical support to salivary glands.
Activity-3:
Take a permanent slide of columnar
epithelium from the slide box and observe
it under the microscope.
Draw the figure that you have
observed under the microscope
How are the cells? Do you find any
hair like projections on the outer
surface of epithelial cells.
This types of cells are present where
ever absorption and secretion occurs. Try
to think where is this type of epithelial
tissues present in your body?
Do you know?The skin is also a kind of
epithelial tissue. Where does nails, and hair
grow from. The scales of fishes, reptiles
and feathers of birds also grow from
epithelium. These are modified epithelial
tissues. You learn more about them in the
chapter: Adaptations in different
Ecosystems.
Connective tissue:
If you tilt your body to any side of
your body, what will happen to your
internal organs? Is there any displacement?
The internal organs are located at specific
places without any displacement in organs
due to connective tissues. The tissueconnect organs and muscles. These tissuesare called connective tissue.
Connective tissues help in binding the
other tissues and organs together and
provide a frame work and support to various
organs in the body. These tissues also play
a major role in the transport of material
from one tissue to another. They also help
in the body defence, body repair and
storage of fat. There are different types of
connective tissues, each performing a
different function.
How do glasswear items carry for
longer distance?
Areolar tissue is one type of
connective tissue which joins different
tissues. It helps in packing and helps to keep
the organs in place. These cells are called
fibroblasts. These are the major
components in this type of connective
tissue. These cells secrete fibrous material
which holds the other tissue in position.
These cells also help in repair of the tissues
when they are injured.
Areolar Tissue
The muscles in our body are attached
to the skin and bone by this type of tissue.
We can see this type of tissue around blood
vessels and nerves.
Why do old people shiver more in winter when than youngsters? Is there any special arrangement to prevent the escape of heat
energy during winter? Fat storing adipose tissue is found below the
skin and between internal organs. The cells of this tissue are filled with fat globules. Storage of fat also acts as insulator. Are all tissues in our body smooth and soft? Which tissue gives definite shape to
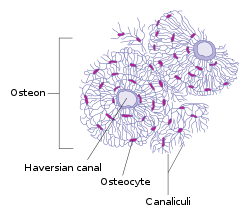
body of vertebrae? Bone is another type of connective tissue; it forms the frame work that supports the body. It is a major component of the skeletal system of several vertebrae
(except some fishes like sharks).
Cartilage is a type of connective tissue
found in the joints of bones, tip of ribs, tip
of the nose, external ears and in trachea.
Embryos of several vertebrae do not have
bone but have cartilage. The entire skeleton
of fishes like sharks is made of cartilage.
Cartilage is hard but not as hard as bone
How two bones are connected at joints?
Ligament is yet another type of
connective tissue that connects bones at
the joints and holds them in position. It is
made up of large number of fibres. These
fibres are made up of a protein called
collagen. This is very elastic in nature.
Activity-4:
Invite a scientist or doctor to your
place. Record an interview about blood
structure and its functions. It is important
to make a questionnaire inorder to conduct
interview. After completion of interview,
prepare a booklet about blood and keep it
in the class room library or display it on
the bulletin board.
It differs from other types of
connective tissues. There are different
types of cells in blood and each one has a
different function. All the cells in the blood
float freely in the plasma. Extra cellular
space is filled with fluid called plasma.
There are no fibres in blood.
Blood:
Blood is also a tissue which is having
different components. Let us know more
about blood.
There is a red stream that flows in
closed canals in our body. Think what is it?
The red stream that flows in closed tubes
in our body is blood. It is also a type of
connective tissue. Blood explains many
things about us. Blood is the source to
identify our wellness or illness. It is very
interesting to know about the blood current
in our body. There is highly sophisticated
and well developed mechanism to circulate
the blood to the entire body. Our heart pumps
nearly 36 thousand litres of blood to a
distance of nearly 20 thousand kilometers
in the time period of 24 hours. Blood is red
in colour. Do you agree with the statement
that all animals carrying red blood are your
blood relatives? The blood is always not red
in all animals. The cockroach has white
blood where as there is blue coloured blood
in snail. It is really a wonder that blood
appears in different colours.
Normal adult human beings have about
5 litres of blood. A chief component in
blood is water, which is stored in the
plasma.
Besides water, it also has several
nutrients such as glucose, amino acids,
proteins, vitamins, hormones, required for
the body and also excretory products such
as lactic acid, urea, salts etc. Plasma also
contains factors responsible for blood
clotting. Heparin helps to prevent blood
clotting in blood vessels.
Cells present in blood are corpuscles.
They are three types 1. RBC, 2. WBC,
3. Blood platelets.
Red blood cells also known as
erythrocytes which are red in colour. They
have red coloured protein called
haemoglobin. Because of haemoglobin
blood is red in colour, which helps in the
transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide 1ml
of human blood has about 5 millions of red
blood cells which live for 120 days in
blood.
Taking blood of an adult we can make a
chain of red blood cells around the earth at
equator with 7 circles. When you are in
your mother’s womb your RBC are formed
in the liver and spleen. After your birth
these RBC are generated from the bone
marrow of long bones. In mammals, mature
red blood cells are without nucleus.
Muscle Tissue:
If you are wounded deeply, a deep scar
would form at the place of wound? If we
are wounded on skin, a lighter scar would
form. Why? For the reason, that the skin
cells have regenerating character. Think
about the muscle cell. Will they get
regenerated like epithelial cells?
Muscles are responsible for the
movements of hands and legs and also of
several internal organs such as intestine and
heart. Small amounts of muscle tissues also
present in blood vessels. These helps in
increasing or decreasing the diameter of
the blood vessel and thus the blood flows.
Heart is made of only one type muscle cells
and they help in pumping the blood.
Striated muscles
How do muscles contract and relax?
Muscular tissue consists of elongated
cells called muscle fibres. This tissue is
responsible for movement in our body.
Muscles contain special protein called
contractile proteins which contract and
relax to cause movement.
During winter, body shivers. Why?
When the body is exposed to cold air,
we shiver. During shivering muscles
contract and relax producing large amount
of heat. This keeps the body hot.
Based on their structure, location and
function, muscles are three types. They are
striated muscle, non-striated muscle,
cardiac muscle.
We can move some muscles by our
conscious effort. For example the muscle
present in inner limbs move according to
our wish and will Such muscles are called
voluntary muscle. These muscles also
called as skeletal muscles as they are
mostly attached to bones and help in body
movement; these muscles show alternate
light and dark bands or striations. As a result,
they are also called striated muscle. The
cells of this tissue are long, cylindrical, un
branched and have many nuclei in the
cytoplasm (multi nucleated).
Nervous Tissue:
If you put your fingers in a glass of hot
water, how do you feel?
How would you know the water is hot
or cold? If you put your leg on a sharp edged
stone while walking, how will you feel?
The feelings like the above situations
is because of specialized mechanism in our
body. It works like electric current passing
through wires. Brain, spinal cord and nerves
play active role in this mechanism.
Nerve cell
Cell body or cyton has a large nucleus
and cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains
granular structure called Nissal’s granules.
There are some projections arising
from cell body. These are called dendrite.
They are sharp, branched, more in number.
One projection of the cyton is somewhat
longer than remaining projections.
This is called axon. Some nerve cells have axon
covered with sheath like structure. This
sheath is called as Myeline sheath. Gas or
nodes present at regular intervals on
myeline sheath are known as Ranvier
Nodes.
Axon of a nerve cell is connected with
Dentrites of a near by nerve cell to form a
web like structure throughout bod











No comments:
Post a Comment